In today’s digital age, reCAPTCHA has become a ubiquitous tool used by websites to verify human users and prevent automated bots from accessing their content. With its simple I’m not a robot checkbox or image recognition tasks, it seems like an innocuous security measure. However, as the world becomes increasingly reliant on this technology, it is important to consider the potential risks associated with reCAPTCHA. From concerns about data privacy and tracking to accessibility issues for individuals with disabilities, exploring the dangers lurking behind this seemingly innocent feature is crucial in understanding the broader implications of its use.
What is reCAPTCHA and how it works?
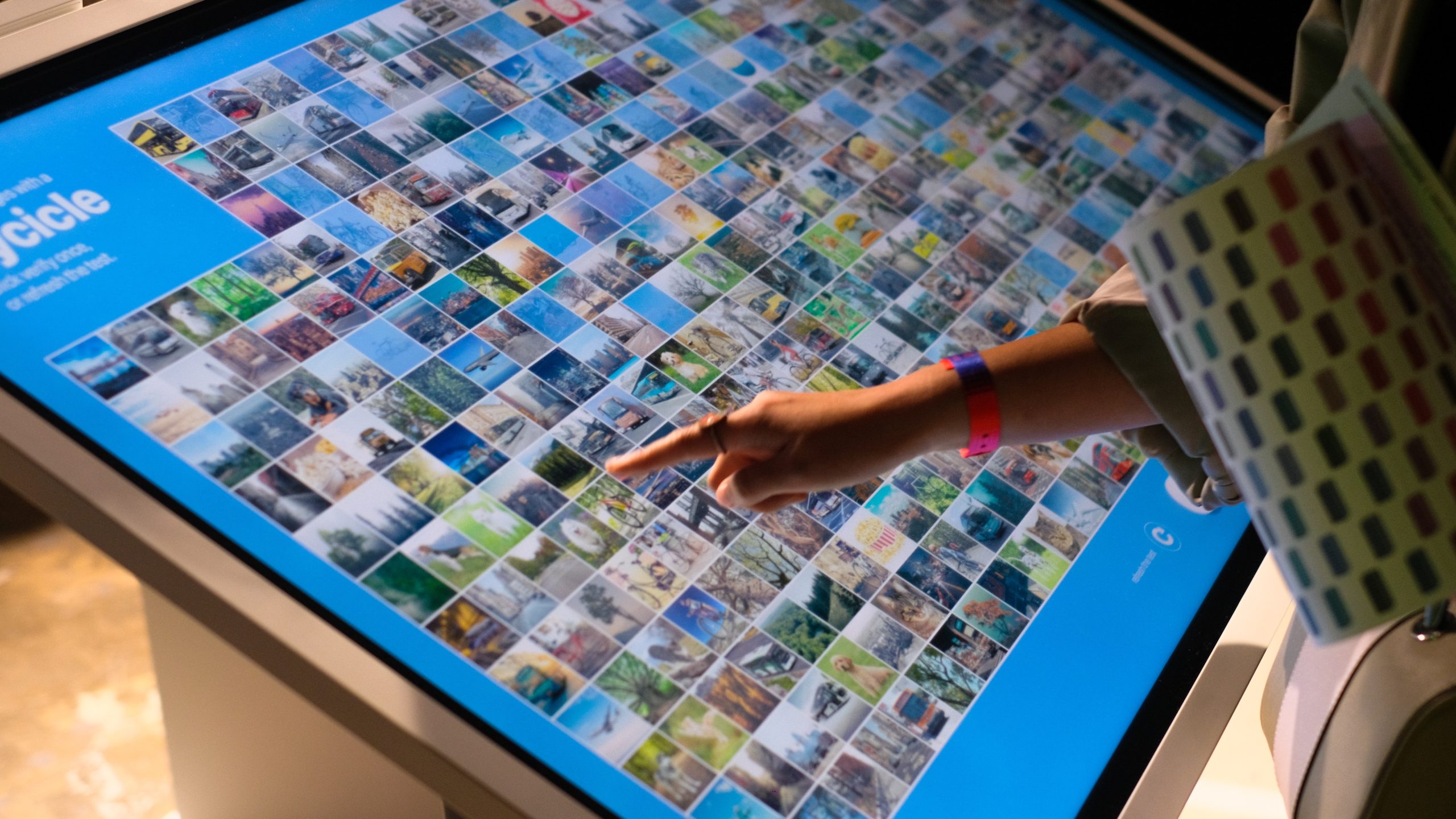
reCAPTCHA, developed by Google, is a widely-used security measure on websites that aims to distinguish between human users and malicious bots. Its main purpose is to prevent automated programs from abusing the website’s functionalities, such as creating multiple accounts or spamming comments sections. By presenting users with a challenge in the form of distorted text or images, reCAPTCHA forces them to prove their humanness through pattern recognition abilities.
Behind its seemingly simple concept lies a complex process involving sophisticated algorithms. When you come across a reCAPTCHA challenge, your response is sent back to Google’s servers for analysis. The system compares your answer with those provided by countless other users encountering similar challenges. This collective feedback helps train AI models and improve them over time. Interestingly, while humans easily recognize patterns like street signs or store fronts in these image-based challenges, this also serves another purpose: helping Google digitize books by having people transcribe hard-to-read words from scanned texts.
By providing a secure barrier against bots, reCAPTCHA ensures the online safety of both website owners and genuine users. Nonetheless, some concerns have been raised regarding privacy and accessibility issues associated with this security measure.
 Security vulnerabilities: Potential weaknesses in reCAPTCHA
Security vulnerabilities: Potential weaknesses in reCAPTCHA
Security vulnerabilities in reCAPTCHA are a topic of concern for users and website owners alike. While the popular Google service is designed to protect against bot attacks, it is not completely foolproof. One potential weakness lies in the audio challenge option offered by reCAPTCHA. Hackers can use automated voice recognition software to bypass this security measure, rendering the audio challenge ineffective.
Another vulnerability arises from the fact that reCAPTCHA relies on machine learning to determine if a user is human or not. This means that its effectiveness hinges on a database of previously identified patterns and behaviors. If hackers can exploit any loopholes or blind spots in this database, they could potentially trick reCAPTCHA into believing they are legitimate users even when they are not.
Ultimately, while reCAPTCHA provides an added layer of security for websites, it is important for both users and website owners to be aware of these potential weaknesses. Implementing additional security measures alongside reCAPTCHA could help mitigate some of these risks and ensure comprehensive protection against various types of attacks.
Privacy concerns: Collection and use of user data
The collection and use of user data has always been a topic of concern in the digital age, and reCAPTCHA is no exception. While its main purpose is to differentiate between humans and bots, there are growing concerns about how extensive the data collection process can be. In order to accurately determine whether a user is human or not, reCAPTCHA often relies on tracking various elements of their online behavior, such as mouse movements and other browser activities. This level of surveillance raises questions about privacy invasion and the ethical implications of using this technology.
Additionally, it’s important to consider who has access to this collected data. While Google claims that they do not use reCAPTCHA data for personalized advertising purposes, it still remains unclear what exactly they do with the information they gather. There’s always a risk that third parties or hackers could gain unauthorized access to this sensitive data, leading potentially compromising situations for users. The underlying concern here is that users have little control over how their information is being used and shared once it enters the realm of reCAPTCHA.
Furthermore, the user profiling aspect comes into play when discussing privacy concerns related to the collection and use of user data through reCAPTCHA. By monitoring user behavior patterns across different websites that implement reCAPTCHA, these interactions can be stored alongside other collected browsing history information by companies like Google.
 Accessibility issues: Impact on users with disabilities
Accessibility issues: Impact on users with disabilities
Accessibility issues have a profound impact on users with disabilities, preventing them from accessing and engaging with online content. While reCAPTCHA may be seen as a security measure for websites, it poses significant barriers to individuals who are visually impaired or have other disabilities. The visual and audio-based puzzles used in reCAPTCHA can be extremely challenging for those with limited vision or hearing, rendering the verification process nearly impossible.
Moreover, the time-sensitive nature of reCAPTCHA can exacerbate accessibility challenges. Users who require more time to complete tasks due to cognitive or physical disabilities may find themselves locked out of websites that implement reCAPTCHA if they cannot solve the puzzles within the allotted timeframe. This restriction not only excludes people with disabilities but also sends a negative message about inclusion and equal access online. It is essential for website developers and designers to prioritize accessibility by adopting alternative solutions that do not exclude individuals with disabilities from accessing their content securely.
User frustration: Challenges and annoyances of reCAPTCHA
One of the most frustrating aspects of reCAPTCHA is the difficulty in accurately interpreting and completing the verification tasks. While the purpose of reCAPTCHA is to distinguish between human users and automated bots, it often feels like a test designed for superhuman capabilities. The distorted text, blurry images, and ambiguous checkboxes can leave users feeling perplexed and annoyed. Not only does this process slow down website interactions, but it can also be particularly challenging for users with visual impairments or cognitive difficulties.
Furthermore, reCAPTCHA poses challenges when it comes to accessibility and inclusivity. While web developers are encouraged to implement accessible alternatives such as audio CAPTCHAs for visually impaired users or alternative options for individuals with motor disabilities, these options are not always readily available or easily accessible. This means that certain groups of people may face even greater frustrations while trying to navigate through websites using reCAPTCHA. Considering the increasing emphasis on digital inclusion and equal access for all internet users, these limitations highlight an inherent flaw in relying solely on reCAPTCHA as a means of verifying user authenticity.
In conclusion, while reCAPTCHA serves a legitimate purpose in protecting websites from spam and malicious activity, its pitfalls cannot be ignored. The frustration experienced by users due to its design complexities and lack of accessibility should prompt website owners and developers to explore alternative authentication methods that address both security concerns as well as user experience considerations. By doing so, we can create a more inclusive online environment without sacrificing security measures against automated bots.
 Alternatives: Other methods for preventing spam and bots
Alternatives: Other methods for preventing spam and bots
While reCAPTCHA may be the most well-known method for preventing spam and bots, there are other alternatives that should not be overlooked. One such alternative is Honeypots. This technique involves creating hidden fields on web forms that only bots can see. When a bot fills out these fields, it identifies itself as non-human, allowing the website to prevent the form from being submitted. Honeypots have proven to be effective in deterring bots without causing any inconvenience to legitimate users.
Another alternative method is Device Fingerprinting. This approach focuses on analyzing the unique characteristics of a device or browser used by a user to access a website. By examining details like IP address, screen resolution, and installed plugins, device fingerprinting can help determine if a visitor is likely human or bot-controlled. While this method relies more on behind-the-scenes analysis rather than direct user interaction like reCAPTCHA does, it provides an additional layer of security against spam and bot attacks.
Exploring these alternatives can offer new approaches for preventing spam and bots while avoiding some of the potential risks associated with reCAPTCHA’s data collection practices. By staying up-to-date on evolving technologies aimed at combating malicious activities online, websites can implement more comprehensive protection measures while ensuring they maintain usability for genuine users.
Conclusion: Weighing the risks versus benefits of reCAPTCHA
In conclusion, while reCAPTCHA may offer some benefits in terms of protecting websites from bots and ensuring user security, it is crucial to carefully weigh the risks associated with its implementation. The primary concern lies in the data privacy aspect, as reCAPTCHA collects and stores personal information about users. With increasing concerns over online privacy and the potential for this data to be misused or accessed by malicious entities, this is not a risk that should be taken lightly.
Furthermore, relying solely on reCAPTCHA as a security measure may lead to unintended consequences. Studies have shown that certain groups of people, such as those with visual impairments or cognitive disabilities, may struggle to successfully complete reCAPTCHA challenges. This can result in exclusion from important online services and create barriers for these individuals. It is essential for website owners to consider alternative methods or additional layers of security to ensure inclusivity and accessibility without compromising user privacy.
 logo
logo